The drone industry is rapidly evolving, and the UK is at the forefront of this technological revolution. From construction and agriculture to emergency services and environmental monitoring, drones are reshaping industries and creating new opportunities. This article explores the key trends and advancements shaping the future of drones in the UK.
The Sky’s the Limit: How Drones are Changing the UK
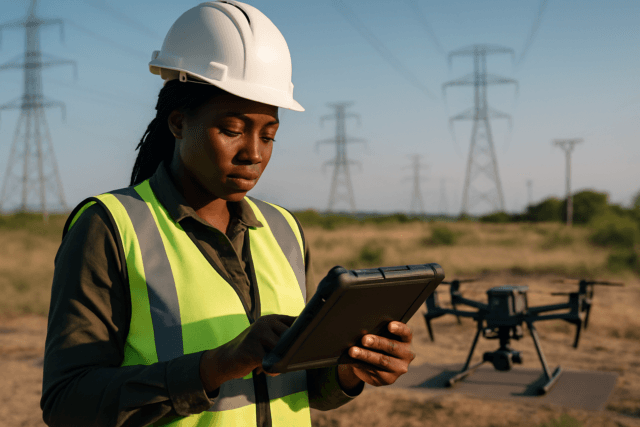
Drones, or Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), have transitioned from military applications to become indispensable tools across various commercial and public sectors. In the UK, drones are streamlining surveys, monitoring construction sites, inspecting infrastructure, and capturing real-time data. PwC estimates that drones could deliver £8.6 billion in annual savings to the UK’s construction and manufacturing sectors by 2030, highlighting their strategic importance.
Why Drones are Taking Off in the UK
Several factors contribute to the increasing adoption of drones in the UK:
- Speed and Efficiency: Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors can capture detailed topographical data in hours, significantly faster than traditional land surveys.
- Improved Safety: Drones can inspect risky areas like scaffolding, roofs, and infrastructure from a safe distance, reducing the need for workers to be exposed to hazardous conditions.
- Cost Savings: By automating tasks and improving efficiency, drones reduce labor costs and project timelines.
Regulatory Landscape: Navigating the UK Skies
The UK Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) is actively updating drone regulations to support safe growth and innovation in the sector. Recent changes include:
- Simpler Rules: Clearer and simpler rules for drone operations, including revised sub-categories in the ‘Open’ category and a new weight limit of 100g for ‘toy’ drones.
- Increased Education: Mandatory online Flyer ID training extended to users of drones over 100g, with improved guidance.
- Product Standards: Introduction of drone product standards via class-marking to improve safety and security.
- Remote ID: Implementation of Direct Remote ID requirements to broadcast identification and location data.
- Specific Operations Risk Assessment (SORA): The CAA is adopting the SORA methodology to evaluate higher-risk drone operations, standardizing safety across the industry.
These regulatory updates aim to create a world-leading environment that balances safety, security, and innovation, fostering sustainable growth in the unmanned aircraft sector.
Key Trends Shaping the Future of Drones
1. AI-Powered Autonomy
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming drone operations by enabling autonomous flight and real-time decision-making. AI-powered drones can:
- Optimize Flight Paths: Adjust flight paths dynamically based on environmental changes and real-time data.
- Perform Complex Missions: Execute adaptive missions in real-time, reducing risks in hazardous environments.
- Enhance Situational Awareness: Use sensor fusion and environmental awareness to operate safely in complex environments.
- Swarm Intelligence: Operate multiple drones as a coordinated unit, making real-time decisions without human intervention.
2. BVLOS Operations
Beyond Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) operations are becoming more feasible, unlocking new opportunities for commercial and public sector drone applications. The FAA Reauthorization Act of 2024 has increased pressure for BVLOS operations through rulemaking rather than waiver-based operations. BVLOS operations will transform:
- Logistics and Delivery: Enabling long-distance drone deliveries.
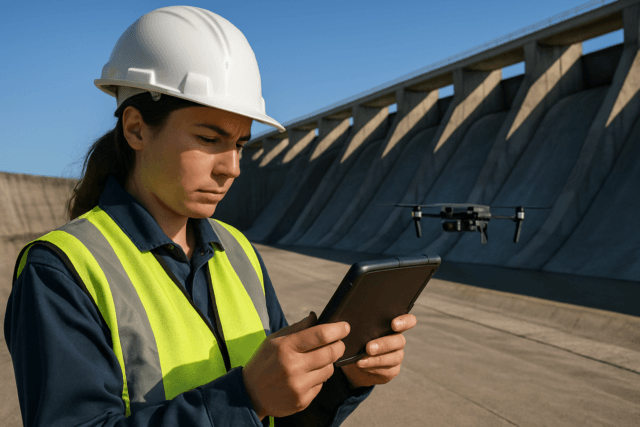
- Infrastructure Inspection: Facilitating remote inspections of bridges, power lines, and pipelines.
- Emergency Response: Improving response times and expanding search and rescue capabilities.
3. Enhanced Imaging and Sensors
High-resolution cameras and sensors are pushing the boundaries of drone photography, videography, and data collection. Drones can now capture:
- 8K Footage: Delivering cinema-quality visuals for filmmaking at a fraction of the cost.
- Thermal Imaging: Monitoring wildfires, tracking hotspots, and identifying heat signatures.
- Multispectral Data: Driving advanced crop monitoring, targeted fertilizer application, and real-time yield estimations in agriculture.
- LiDAR Sensors: Creating detailed 3D models of terrain and infrastructure.
4. Integration with Smart Cities
Drones are becoming an integral part of smart city ecosystems, contributing to traffic management, public safety, and urban planning. Key applications include:
- Traffic Monitoring: Monitoring traffic congestion and providing real-time updates to city planners.
- Emergency Response: Assisting emergency services in assessing situations faster and more efficiently.
- Environmental Monitoring: Tracking pollution levels and assessing environmental impact.
- Infrastructure Inspection: Inspecting bridges, buildings, and other critical infrastructure.
5. Drone Delivery Services
Drone delivery is finally becoming mainstream, with increasing demand for faster and more efficient logistics solutions. The global delivery drones market is projected to grow from $1.8 billion in 2023 to $12.3 billion by 2028, driven by:
- E-commerce Growth: Meeting the increasing demand for quick and efficient delivery of goods.
- Medical Deliveries: Transporting urgent medical supplies in urban and remote areas.
- Last-Mile Delivery: Providing cost-effective and timely delivery of parcels and food.
6. Data Security and Mapping
Data security is a critical concern for drone mapping and geographic information systems (GIS). Companies are prioritizing data security by:
- Local Processing and Storage: Keeping processing and storage local to maintain security and confidentiality.
- Cybersecurity Measures: Implementing robust cybersecurity measures to protect against cyber threats.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to data protection regulations and privacy standards.
7. Counter-Drone Technology
The increasing use of drones has also led to the development of counter-drone technology to mitigate security threats. Governments and defense agencies are investing in:
- Jamming Systems: Disrupting drone communication signals.
- Detection Sensors: Identifying and tracking unauthorized drones.
- Drone Capture Mechanisms: Intercepting and capturing rogue drones.
Drones in Action: Real-World Applications in the UK
Construction
Drones are transforming construction sites by:
- Streamlining Surveys: Capturing detailed topographical data in hours.
- Monitoring Site Progress: Tracking construction progress and identifying potential delays.
- Inspecting Structures: Inspecting scaffolding, roofs, and infrastructure from a safe distance.
- Transporting Small Equipment: Reducing time and labor associated with ground transportation.
Agriculture
In agriculture, drones are used for:
- Crop Monitoring: Providing real-time data on crop health and growth.
- Targeted Fertilizer Application: Applying fertilizers and pesticides with precision.
- Yield Estimation: Estimating crop yields and optimizing harvesting schedules.
Emergency Services
Drones are becoming essential tools for emergency services, assisting in:
- Search and Rescue: Covering vast disaster zones and pinpointing survivors quickly.
- Wildfire Monitoring: Tracking wildfire perimeters and relaying real-time data to incident command centers.
- Traffic Incident Response: Assessing traffic incidents and providing real-time updates.
Environmental Monitoring
Drones are playing a critical role in environmental monitoring by:
- Tracking Deforestation: Monitoring deforestation and illegal logging activities.
- Pollution Monitoring: Assessing air and water quality.
- Wildlife Monitoring: Tracking wildlife populations and behaviors.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the future of drones in the UK looks promising, there are challenges to address:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Clear and predictable regulations are essential for fostering a stable investment environment.
- Technological Barriers: Continued research and development are needed to address limitations in battery life, payload capacity, and communication range.
- Skilled Workforce: Addressing the lack of a skilled workforce through training and education programs.
- Public Perception: Fostering public trust by demonstrating responsible drone operations and addressing privacy concerns.
By addressing these challenges and capitalizing on emerging opportunities, the UK can solidify its position as a global leader in the drone industry.
The Future is Here: Embracing the Drone Revolution
The drone industry in the UK is poised for significant growth and innovation. With advancements in AI, BVLOS operations, enhanced imaging, and smart city integration, drones are transforming industries and improving lives. By embracing these changes, fostering collaboration, and promoting responsible operations, the UK can unlock the full potential of drone technology and create a brighter, more efficient future.