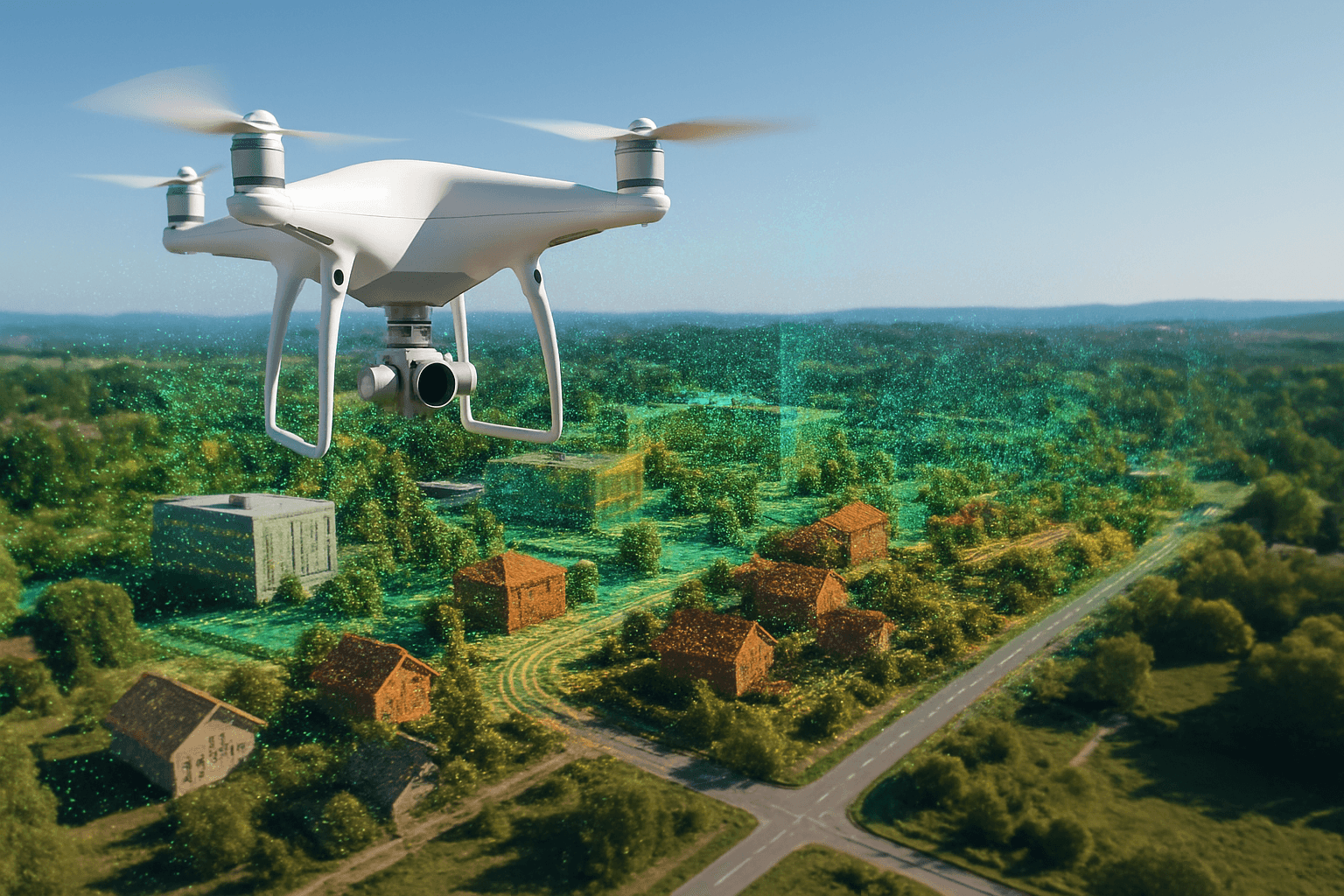
Drones have revolutionized various industries, and one of the most impactful applications is creating point clouds. A drone point cloud is a detailed, three-dimensional representation of an area or object, generated from data captured by drones. This technology has transformed surveying, construction, environmental monitoring, and many other fields, offering unprecedented accuracy, efficiency, and safety. This comprehensive guide explores the ins and outs of drone point clouds, covering everything from the basics to advanced applications.
What is a Point Cloud?
A point cloud is a set of data points in a three-dimensional coordinate system. Each point has X, Y, and Z values, defining its position in space. These points collectively represent the surfaces of objects or terrain features. Point clouds can range from a few thousand to billions of points, depending on the resolution and area covered. The higher the density of points, the more accurate and detailed the representation. Survey-grade point clouds typically have a distance of 2-3mm between points.
How Drones Create Point Clouds
Drones create point clouds using two primary methods: LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and photogrammetry.
LiDAR
LiDAR technology involves emitting laser pulses from a sensor on the drone to the ground and measuring the time it takes for the pulses to return. By combining this data with inertial measurement and satellite positioning, the drone’s LiDAR system determines the precise location of each point in space. LiDAR is known for its accuracy and ability to penetrate vegetation, making it ideal for forestry and topographic mapping.
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry uses high-resolution photographs captured by the drone’s camera to recreate a survey area. Distinct features are identified in multiple overlapping images, and their locations are measured using the camera sensor’s position. This method is more cost-effective than LiDAR, with hardware and software being considerably lower priced. Photogrammetry creates point clouds with enough accuracy for most sitework and mining applications and requires minimal training to capture drone data.
Key Characteristics of Drone Point Clouds
Several characteristics define the quality and usability of drone point clouds:
Point Density
Point density refers to the number of data points per unit area. Higher point density results in more detailed and accurate representations of the surveyed area. Factors influencing point density include the LiDAR system’s resolution, drone altitude, and data collection speed.
Accuracy
Accuracy pertains to how closely the measured points correspond to their true positions in the real world. High accuracy is essential for applications requiring precise measurements, such as engineering and construction projects. Accuracy depends on the quality of the LiDAR system, GPS, IMU data, and data processing techniques.
Resolution
Resolution relates to both point density and the system’s ability to distinguish between closely spaced objects. High-resolution point clouds can capture fine details, making them suitable for vegetation analysis or detailed urban development mapping.
The Process of Creating Drone Point Clouds
Creating a drone point cloud involves several key steps:
- Planning: Careful flight planning is crucial for efficient data acquisition. This includes determining the flight path, altitude, and camera settings.
- Data Acquisition: The drone, equipped with either a LiDAR sensor or a high-resolution camera, follows the planned flight path to scan the target area.
- Data Processing: Raw data is imported and preprocessed, followed by filtering to remove noise and irrelevant points.
- Point Cloud Generation: Specialized software assembles the data points into a usable form, either by adding context to laser pulses (LiDAR) or generating points based on multiple photos (photogrammetry).
Software for Processing Drone Point Clouds
Various software solutions are available for processing drone point clouds, each offering unique features and capabilities. Here are some popular options:
- DJI Terra: A 3D model reconstruction software with photogrammetry at its core, supporting accurate 2D and 3D reconstruction and data processing through DJI LiDAR. It’s a perfect match for DJI Enterprise drones and payloads.
- Agisoft Metashape: Aims to deliver ‘Intelligent Photogrammetry’ with fast and accurate processing, capable of handling over 50,000 images.
- Pix4DMapper: A professional software for creating georeferenced 2D maps and 3D models with sub-centimeter accuracy, offering various software tailored to specific applications like construction and agriculture.
- WebODM: An open-source drone mapping software that is free to install, allowing users to generate maps, point clouds, 3D models, and DEMs from aerial images.
- LSS Elite: Designed for processing large datasets from laser scanners or drones, offering tools for point cloud creation, outlier recognition, terrain extraction, and orthophoto generation.
- LiDAR360: A comprehensive LiDAR point cloud processing and analysis software developed by GreenValley International, tailored for terrain analysis, forestry management, and power line inspection.
Applications of Drone Point Clouds
Drone point clouds have a wide array of applications across various industries:
Surveying and Mapping
- Land Surveying: Quickly generate detailed topographical maps of areas, ideal for clients needing fast and accurate surveys.
- Topographic Mapping: Create precise 3D models of terrain, essential for urban planning, environmental monitoring, and construction.
- Volumetric Calculations: Determine the volume of stockpiles, excavations, and other features with high accuracy.
- Corridor Mapping: Map linear infrastructure such as roads, railways, and pipelines for planning, maintenance, and risk assessment.
Construction and Engineering
- Infrastructure Planning: Architects and engineers can gain detailed insights for innovative and feasible designs.
- As-Built Documentation: Create accurate 3D models of existing structures to inform renovation and construction planning.
- Progress Tracking: Monitor earthwork progress, material movement, and overall project progress.
Environmental Monitoring
- Forestry: LiDAR can penetrate dense foliage to provide surface data, which is invaluable for forest management and analysis.
- Coastal Mapping: Monitor coastal hazards, flood risks, and shoreline changes with high-resolution LiDAR data.
- Environmental Analysis: Detailed topographical data can assist environmentalists in understanding terrains, aiding conservation and research.
Cultural Heritage
- Heritage Conservation: Historic structures can be mapped with precision, aiding restoration and preservation efforts.
Emergency Services
- Disaster Modeling: Versatile resource for disaster modeling.
- Emergency Response: Drones provide quick and safe surveys of incident sites.
Other Applications
- Power Infrastructure: Survey new utility infrastructure and inspect existing power lines, especially in remote areas.
- Mining: Monitor site conditions, track material movement, and calculate volumes in mining operations.
- Agriculture: Assess crop health, plan agricultural routes, and optimize resource allocation.
- Oil and Gas Industry: Create high-detail digital twins for optimizing operations, reducing costs, and improving safety.
- Archaeology: Detect archaeological features through detailed terrain analysis.
- Legal and property documentation: Point Cloud Surveys can play a pivotal role in boundary delineations and land disputes.
Advantages of Using Drone Point Clouds
Drone point clouds offer several advantages over traditional methods:
- Enhanced Precision: Drones equipped with LiDAR technology capture vast areas in great detail, ensuring point cloud surveys are exhaustive and accurate.
- Increased Accessibility: Drones can access hard-to-reach locations, ensuring every area is recorded.
- Efficiency and Time-Saving: Drones survey areas quickly, reducing the time and resources traditionally required for terrestrial methods.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Utilizing drones translates to fewer ground personnel and equipment, resulting in cost savings.
- Improved Safety: Aerial surveys can be conducted from a safe distance, reducing the risk of injury.
- Comprehensive Data: Generate topographic maps, volumetric calculations, digital terrain models, and full 3D visualizations from a single survey.
- Vegetation Penetration: LiDAR can penetrate dense vegetation to capture ground levels beneath trees.
- Remote Collaboration: Point cloud platforms enable remote collaboration, minimizing travel and reducing carbon footprint.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the numerous benefits, there are challenges to consider when working with drone point clouds:
- Data Processing Complexity: Processing point cloud data requires specialized software and expertise.
- Accuracy Limitations: The accuracy of point clouds depends on the quality of the sensors and data processing techniques.
- Environmental Factors: Wind, sunlight, and other environmental conditions can impact data quality.
- Regulatory Compliance: Drone operations are subject to regulations, including licensing and airspace restrictions.
The Future of Drone Point Clouds
The future of drone point clouds looks promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and increasing adoption across industries. Some key trends include:
- Improved Sensor Technology: Advancements in LiDAR and camera technology will lead to higher resolution and more accurate point clouds.
- Automated Processing: AI-powered software will automate data processing, making it faster and more efficient.
- Real-Time Processing: Onboard processing capabilities will enable real-time point cloud generation, facilitating immediate decision-making.
- Integration with BIM: Seamless integration with Building Information Modeling (BIM) will streamline workflows in construction and infrastructure projects.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Cloud platforms will provide easy access to point cloud data and processing tools, fostering collaboration and innovation.
Drone Point Clouds in the UK
In the UK, drone point clouds are transforming industries such as construction, infrastructure, and environmental management. Companies like Virtuscan and AUAV are offering specialized drone survey services, providing high-quality point cloud data for various applications.
The use of drone LiDAR surveys is gaining traction due to their ability to deliver detailed terrain models, accurate measurements through dense foliage, and comprehensive point cloud data sets. The UK Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) regulates drone operations, ensuring safety and compliance.
Conclusion
Drone point clouds represent a significant advancement in 3D mapping and surveying. Their ability to capture detailed, accurate data quickly and safely is revolutionizing industries worldwide. Whether it’s for creating topographic maps, monitoring construction progress, or analyzing environmental changes, drone point clouds provide valuable insights for informed decision-making. As technology continues to evolve, the potential applications of drone point clouds will only expand, making them an indispensable tool for professionals across various sectors.